Building a RAG-Powered AI Chatbot for Single-Cell Analysis - Part 3: CLI Query Engine
Published:
In this part, we will connect the knowledge base we built in part 2 with an OpenAI LLM, transforming scOracle into a functional AI-powered chatbot for single-cell analysis!
OpenAI API Key
To utilize an OpenAI LLM, an API key is required. Here’s how:
- Opening an OpenAI account at https://platform.openai.com/
- Create a key at API key settings
- Store the key as an environment variable named
OPENAI_API_KEY:export OPENAI_API_KEY="your-key-here"I added this line to my ~/.bashrc so I wouldn’t need to re-run it in every session.
Once set, I can now access the key in the scOracle CLI script:
#### cli.py
import openai
# === OPENAI API KEY ===
openai.api_key = os.getenv("OPENAI_API_KEY")
if openai.api_key is None:
raise ValueError("Please set the OPENAI_API_KEY environment variable.")
Retrieve Chroma vector store
Next, I loaded in the embedded knowledge base created in the previous part. This allows the chatbot to access the indexed documents through the Chroma vector store.
import chromadb
from llama_index.core import VectorStoreIndex
from llama_index.vector_stores.chroma import ChromaVectorStore
CHROMA_PATH = "../chroma_db"
COLLECTION_NAME = "scoracle_index"
# === Retrieve the Chroma vector store ===
chroma_client = chromadb.PersistentClient(path=CHROMA_PATH)
collection = chroma_client.get_or_create_collection(COLLECTION_NAME)
vector_store = ChromaVectorStore(chroma_collection=collection)
index = VectorStoreIndex.from_vector_store(vector_store)
Set up LLM and chat engine
With the indexed knowledge base loaded, I configured the LLM and instantiated a ChatEngine from LlamaIndex. I used OpenAI’s lightweight gpt-4o-mini model with a zero-temperature setting for consistent, factual responses. I also set the top_k parameter to 8, which controls how many of the most relevant document chunks are retrieved for each query.
from llama_index.core import Settings
from llama_index.embeddings.huggingface import HuggingFaceEmbedding
from llama_index.llms.openai import OpenAI
TOP_K = 8 # retrieve the 8 most similar chunks
Settings.embed_model = HuggingFaceEmbedding(model_name="sentence-transformers/all-MiniLM-L6-v2")
# === Set up LLM and chat engine ===
llm = OpenAI(
model="gpt-4o-mini",
temperature=0.0,
system_prompt="""
You are scOracle, a scientific assistant for single-cell RNA-seq analysis.
You can answer technical questions using your knowledge of documentation, code, and tutorials from bioinformatics tools such as Scanpy.
"""
)
chat_engine = index.as_chat_engine(similarity_top_k=TOP_K, chat_mode="best", llm=llm)
Implement chatbot loop
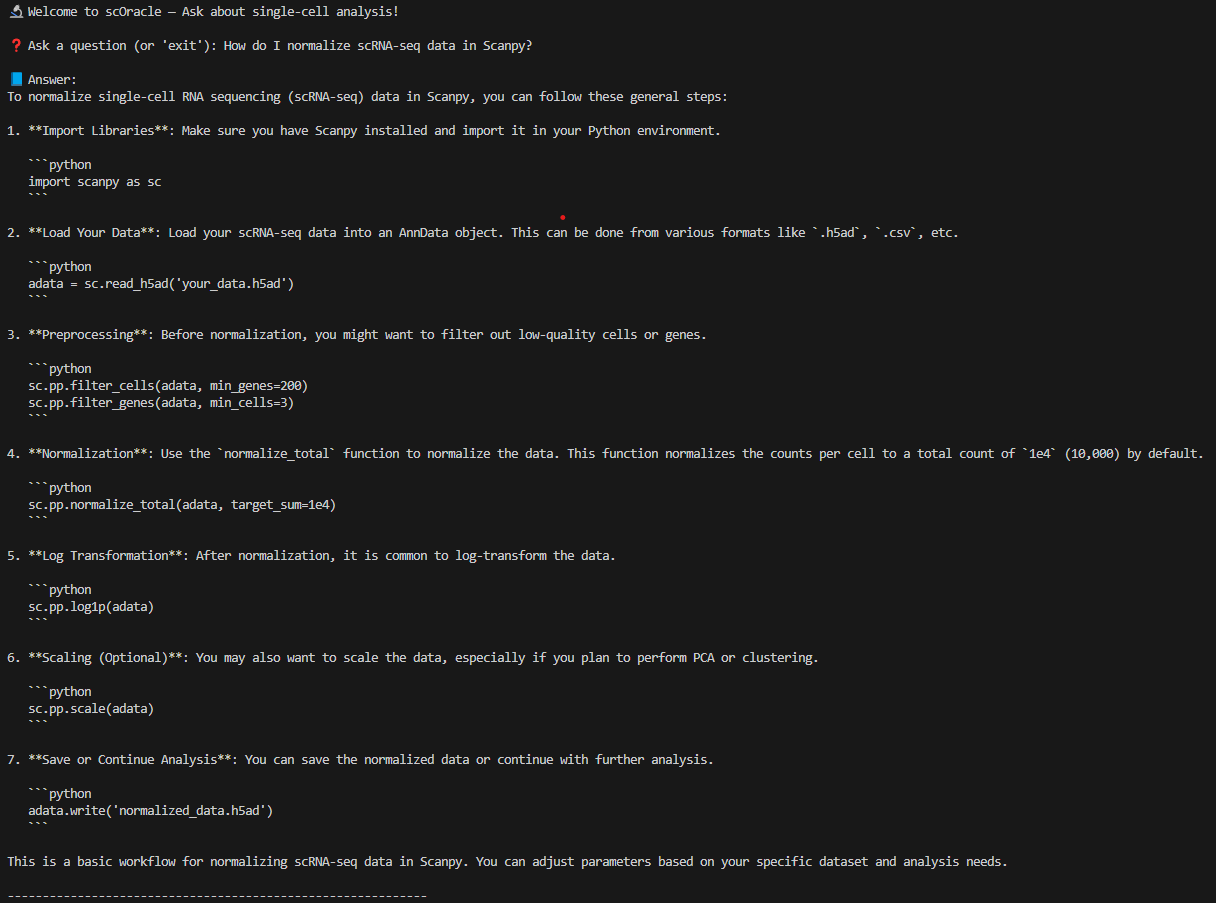
Finally, I implemented a simple chatbot loop to make scOracle functional from the command line. This CLI lets me ask questions and get context-aware answers powered by the indexed Scanpy knowledge base.
import asyncio
async def main():
print("🔬 Welcome to scOracle — Ask about single-cell analysis!\n")
while True:
user_input = input("❓ Ask a question (or 'exit'): ")
if user_input.lower() == "exit":
break
response = await chat_engine.achat(user_input)
print("\n📘 Answer:")
print(response)
print("\n" + "-" * 60 + "\n")
if __name__ == "__main__":
asyncio.run(main())
scOracle in action
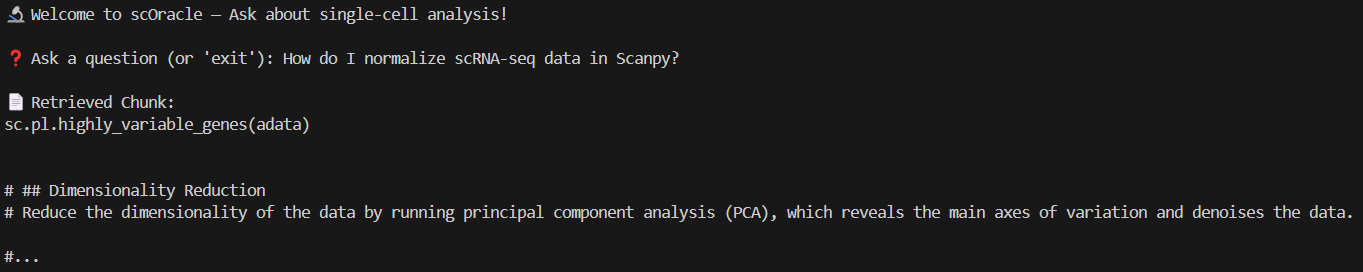
To confirm that RAG is actually working, we can add a print statement to inspect the documents being retrieved:
response = await chat_engine.achat(user_input)
for source_node in response.source_nodes:
print(f"\n📄 Retrieved Chunk:\n{source_node.node.get_content()[:500]}...") # truncate for readability